CoordinateSpace
Representation of a coordinate space, for easy transformations in 3D space related abstractions.
Version: 14b43e9
Canonical type name: codal::CoordinateSpace
Defined within: inc/types/CoordinateSpace.h
Usage & Examples
One common use for this class may be to convert from a standard ENU format into cartesian format for later calculation purposes. In this case, you could create a coordinate space and perform a transform like so (assuming no rotation transform):
//Create a coordinate space with SIMPLE_CARTESIAN.
auto coordinateSystem = CoordinateSpace(CoordinateSystem::SIMPLE_CARTESIAN);
//Perform a transform.
auto enuVector = Sample3D(32, 14, 55);
auto simpleCartesianVector = coordinateSystem.transform(enuVector);
Methods
CoordinateSpace(CoordinateSystem, …)
CoordinateSpace(CoordinateSystem system, bool upsidedown = false, int rotated = COORDINATE_SPACE_ROTATED_0);
Creates a coordinate space of the given coordinate system, optionally making the system flipped or rotated.
Parameters
- coordinateSystem (CoordinateSystem): The coordinate system that this coordinate space uses.
- upsidedown (bool, optional): Whether this coordinate space should be flipped vertically.
- rotated (int, optional): The rotation of the sensor on the PCB. Defines pin 1 as the top left corner. Does not represent an angle, only valid values are defined as COORDINATE_SPACE_ROTATED_*.
transform(Sample3D)
Sample3D transform(Sample3D s);
Transforms a given Sample3D in ENU format into the format defined in this coordinate space.
Parameters
- s (Sample3D): The ENU format sample to convert into this coordinate space.
transform(Sample3D, CoordinateSystem)
Sample3D transform(Sample3D s, CoordinateSystem system);
Transforms a given Sample3D in ENU format into the format defined in the supplied CoordinateSystem system.
Parameters
- s (Sample3D): The ENU format sample to convert into this coordinate space.
- system (CoordinateSystem): The coordinate system to output in.
Returns - The equivalent location of the provided sample s in the current CoordinateSpace, in the format of the provided CoordinateSystem system.
Members
system
CoordinateSystem system;
The CoordinateSystem this coordinate space uses to output transformed samples.
upsidedown
bool upsidedown;
Whether this coordinate system is vertically flipped or not.
rotated
int rotated;
The rotation of this coordinate system, based on the rotation of the sensor on the PCB, defining pin 1 as the top left corner. Does not represent an angle, and defines valid values as COORDINATE_SPACE_ROTATED_*, like so:
#define COORDINATE_SPACE_ROTATED_0 0
#define COORDINATE_SPACE_ROTATED_90 1
#define COORDINATE_SPACE_ROTATED_180 2
#define COORDINATE_SPACE_ROTATED_270 3
Structs
Sample3D
Represents a single three dimensional vector. Defines operator overloads for equality and addition/subtraction.
struct Sample3D
{
int x;
int y;
int z;
Sample3D();
Sample3D(int x, int y, int z);
float dSquared(Sample3D &s);
Sample3D operator-(const Sample3D& other) const;
Sample3D operator+(const Sample3D& other) const;
bool operator==(const Sample3D& other) const;
bool operator!=(const Sample3D& other) const;
};
Enumerations
CoordinateSystem
The types of coordinate system available to the accelerometer.
enum CoordinateSystem
{
RAW,
SIMPLE_CARTESIAN,
NORTH_EAST_DOWN,
EAST_NORTH_UP,
NORTH_EAST_UP = EAST_NORTH_UP, //For legacy compatibility.
};
To make this easier to visualise, the below diagram demonstrates the orientation and direction of the axes with each of these values.
| Simple Cartesian | North East Down |
|---|---|
 | 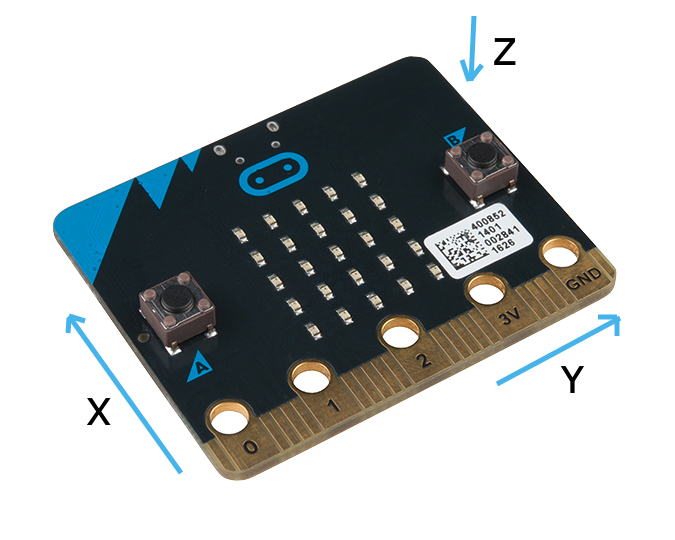 |
Class Definition
class CoordinateSpace
{
public:
CoordinateSystem system;
bool upsidedown;
int rotated;
CoordinateSpace(CoordinateSystem system, bool upsidedown = false, int rotated = COORDINATE_SPACE_ROTATED_0);
Sample3D transform(Sample3D s);
Sample3D transform(Sample3D s, CoordinateSystem system);
};